The first 4TB SSD with QLC memory has been filtered and can become the revolution we expect from this storage technology.
The first 4TB SSD with QLC memory would be close to market, according to a leak.
This is possibly the most critical time for the SSD storage industry; the arrival of the first QLC devices could revolutionize the market.
QLC (quad-level cell), is a NAND storage technology in which each cell has four different levels, so each cell can store four values. So, logically, a QLC NAND memory will enjoy higher data density in the same space; and that translates into larger storage SSDs without physically increasing the size.
This would be the first 4 TB SSD with QLC memory
Micron and Intel have been the two pioneers in this field of QLC memories, and we were already aware that the first units were not far from being launched; although at first, we thought that it would be Micron, with its 5210 ION, that would come onto the market. But there was still a lot of data to be done, such as capacity, or when it would reach consumers.
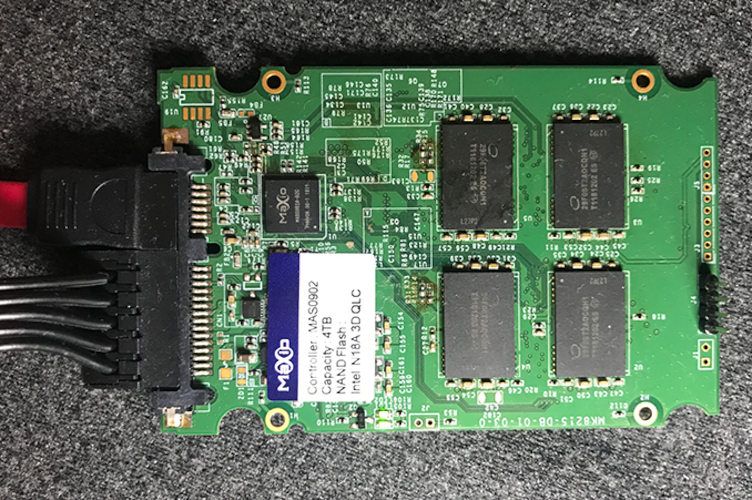
And now Anandtech has got leads on the first possible 4TB SSD with QLC memory to officially hit the market – not for the average user, but for professional environments – but that would be a breakthrough for this technology.
The device discovered has been a 4TB capacity SSD, which uses the new Intel QLC memory chips; however, this will not be an official Intel SSD. The memory controller is from Maxio Technology, a specialized manufacturer, and therefore it would be no surprise if this product were to reach stores all over the world.
However, this will not be soon. The Maxio prototype supports only 500 writes and erases cycles, while the numbers that Intel and Micron have shared are around 1,000 cycles. This means that we are dealing with a prototype, which still has a long way to go.
At least it has helped us to learn more data, such as performance, which was a big question mark; the Maxio model achieves a performance very similar to that of other SSDs, but in this case, we have to take into account the bottleneck of the SATA connection. Only with an NVMe connection model will we know the true performance that QLC memory can achieve.