As we have already published news on new AMD machine. Today, AMD Rome EPYC processor, the new 64-core Rome EPYC processor with 128 threads have appeared in an online database, pointing towards the first chips operating at 1.4 GHz base clock and reaching 2.2 GHz.
AMD announced earlier this year that the 64-core, 128-thread Rome EPYC processors would come onto the market in mid-2019, perhaps paving the way for a big victory against Intel as AMD advances towards a 7nm manufacturing process while its direct competitor in the server segment remains at 14nm.
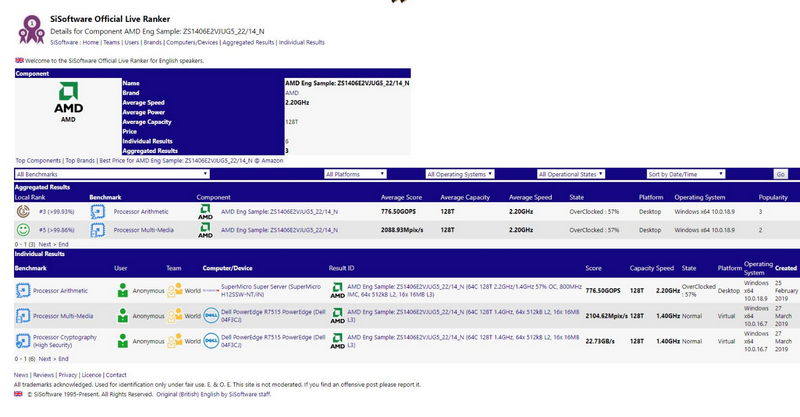
Several submissions to the SiSoft Sandra database regarding the EPYC processor have been published in recent months, most of which carry the descriptor “Z” at the beginning of product identifier ZS1406E2VJUG5_22/14_N. This means that they are qualification samples, implying that the chip approaches the final design closely.
A Dell PowerEdge R7515 dual-socket server lists as the test system. Describing the name of the product, the clock frequencies, the number of cores, threads and that it has 64x512KB L2 cache and 256MB L3 cache are given. While the frequencies may seem low, it is important to remember that the chip has 64 cores. Boosting the frequencies too much in such a large number of cores would result in too much consumption and heat generation.
AMD Rome EPYC processor Heat Problems
For example, the EPYC 7601 with 32 cores and 64 AMD threads has a base frequency of 2.2 GHz and a turbo frequency of 3.2 GHz, indicative to the fact that doubling the Rome cores may require even more thermal reduction enhancements, even with a smaller and more efficient 7nm process. AMD has not announced the TDP ranges for its Rome EPYC processors, however, its predecessors range from 120W to 180W.